Label the diagram of the kidney and nephron below. – In this comprehensive guide, we embark on a journey to label the intricate structures of the kidney and nephron, delving into their functions and the crucial role they play in maintaining our health. Through an engaging exploration, we unravel the complexities of these organs, shedding light on their vital processes and their significance in our overall well-being.
Our kidneys, the unsung heroes of our bodies, perform the remarkable task of filtering waste products and regulating fluid balance. The nephron, the functional unit of the kidney, is a marvel of nature, responsible for the intricate processes of filtration, reabsorption, and secretion.
Together, these components work in harmony to ensure the proper functioning of our bodies.
Label the Diagram of the Kidney
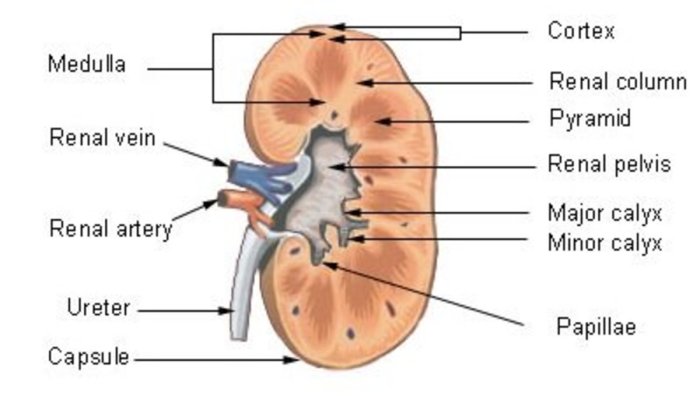
The kidney is a bean-shaped organ located on either side of the spine. It is responsible for filtering waste products from the blood and producing urine. The kidney is divided into two main regions: the renal cortex and the renal medulla.
The renal cortex is the outer layer of the kidney. It contains the glomeruli, which are small clusters of blood vessels where blood is filtered. The renal medulla is the inner layer of the kidney. It contains the tubules, which are small tubes that transport the filtered fluid from the glomeruli to the renal pelvis.
The renal pelvis is a funnel-shaped structure that collects the filtered fluid from the tubules. The calyces are small cups that extend from the renal pelvis and surround the renal pyramids. The renal pyramids are cone-shaped structures that contain the tubules.
The collecting ducts are small tubes that collect the filtered fluid from the tubules and transport it to the renal pelvis. The renal pelvis then transports the filtered fluid to the bladder, where it is stored until it is excreted as urine.
Label the Diagram of the Nephron
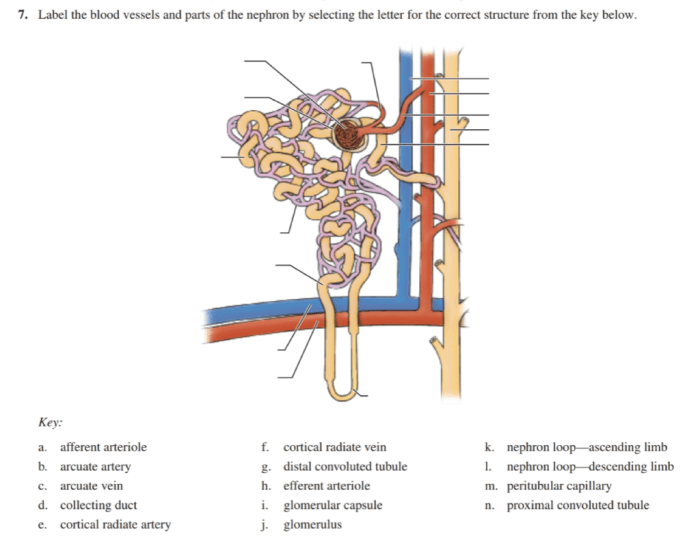
The nephron is the functional unit of the kidney. Each kidney contains about 1 million nephrons. The nephron is responsible for filtering waste products from the blood and producing urine.
The glomerulus is a small cluster of blood vessels where blood is filtered. The proximal convoluted tubule is a small tube that transports the filtered fluid from the glomerulus to the loop of Henle.
The loop of Henle is a U-shaped tube that helps to concentrate the filtered fluid. The distal convoluted tubule is a small tube that transports the concentrated filtered fluid from the loop of Henle to the collecting duct.
The collecting duct is a small tube that collects the concentrated filtered fluid from the distal convoluted tubules and transports it to the renal pelvis. The renal pelvis then transports the concentrated filtered fluid to the bladder, where it is stored until it is excreted as urine.
Create an HTML Table to Label the Kidney and Nephron
| Structure | Function |
|---|---|
| Renal cortex | Contains the glomeruli |
| Renal medulla | Contains the tubules |
| Renal pelvis | Collects the filtered fluid from the tubules |
| Calyces | Small cups that extend from the renal pelvis and surround the renal pyramids |
| Renal pyramids | Cone-shaped structures that contain the tubules |
| Collecting ducts | Collect the filtered fluid from the tubules and transport it to the renal pelvis |
| Glomerulus | Small cluster of blood vessels where blood is filtered |
| Proximal convoluted tubule | Transports the filtered fluid from the glomerulus to the loop of Henle |
| Loop of Henle | Helps to concentrate the filtered fluid |
| Distal convoluted tubule | Transports the concentrated filtered fluid from the loop of Henle to the collecting duct |
Elaborate on the Function of the Nephron
The nephron is the functional unit of the kidney. It is responsible for filtering waste products from the blood and producing urine. The nephron consists of several different parts, each with a specific function.
Glomerular filtration is the process by which blood is filtered in the glomerulus. The glomerulus is a small cluster of blood vessels that is located in the renal cortex. The blood vessels in the glomerulus are very thin, which allows water and small molecules to pass through them, but not larger molecules such as proteins.
The filtered fluid, which is called glomerular filtrate, then flows into the proximal convoluted tubule.
The proximal convoluted tubule is the first part of the nephron that the glomerular filtrate flows through. The proximal convoluted tubule reabsorbs water and solutes from the glomerular filtrate. The reabsorbed water and solutes are then returned to the bloodstream.
The proximal convoluted tubule also secretes waste products into the glomerular filtrate.
The loop of Henle is the next part of the nephron that the glomerular filtrate flows through. The loop of Henle is a U-shaped tube that is located in the renal medulla. The loop of Henle helps to concentrate the glomerular filtrate by reabsorbing water and solutes.
The concentrated glomerular filtrate then flows into the distal convoluted tubule.
The distal convoluted tubule is the final part of the nephron that the glomerular filtrate flows through. The distal convoluted tubule reabsorbs water and solutes from the glomerular filtrate. The reabsorbed water and solutes are then returned to the bloodstream.
The distal convoluted tubule also secretes waste products into the glomerular filtrate.
The collecting duct is the final part of the nephron. The collecting duct collects the glomerular filtrate from the distal convoluted tubules and transports it to the renal pelvis. The renal pelvis then transports the glomerular filtrate to the bladder, where it is stored until it is excreted as urine.
Questions and Answers: Label The Diagram Of The Kidney And Nephron Below.
What is the function of the renal pelvis?
The renal pelvis serves as a funnel-shaped structure that collects urine from the calyces and transports it to the ureter.
What is the role of the loop of Henle in the nephron?
The loop of Henle plays a crucial role in concentrating urine by creating a gradient of increasing osmolarity, allowing for the reabsorption of water and the excretion of concentrated urine.
How does the nephron regulate water and electrolyte balance?
The nephron regulates water and electrolyte balance by selectively reabsorbing or secreting ions and water, ensuring the maintenance of proper fluid volume and electrolyte concentrations in the body.