Cellular respiration, the process by which cells generate energy, is essential for life. This article examines which of the following statements about cellular respiration is true, exploring its significance, key stages, energy production, reactants and products, efficiency and regulation, and role in metabolism.
Delving into the intricacies of cellular respiration, we uncover the mechanisms that drive cellular energy production and sustain life’s processes.
Cellular Respiration Overview

Cellular respiration is a vital metabolic process that occurs in the cells of living organisms, playing a crucial role in generating energy for cellular activities. It involves a series of chemical reactions that convert biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy currency of cells.
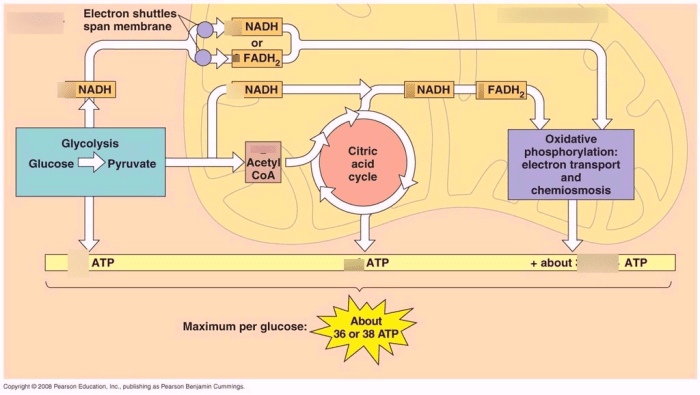
The process consists of three main stages: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle (also known as the citric acid cycle), and the electron transport chain.
Energy Production, Which of the following statements about cellular respiration is true
Cellular respiration is primarily responsible for producing energy for cells. During glycolysis, glucose is broken down into pyruvate, releasing a small amount of ATP. The Krebs cycle further oxidizes pyruvate, generating more ATP, NADH, and FADH2. These molecules are then used in the electron transport chain to pump protons across a membrane, creating an electrochemical gradient.
This gradient drives the synthesis of ATP through ATP synthase.
Reactants and Products
The primary reactants of cellular respiration are glucose and oxygen. Glucose is the main energy source for most cells, while oxygen acts as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain. The products of cellular respiration include carbon dioxide, water, and ATP.
Carbon dioxide is released as a waste product, while water is formed as a byproduct of the electron transport chain.
Efficiency and Regulation
Cellular respiration is a highly efficient process, with approximately 30-40% of the energy in glucose being converted into ATP. The efficiency of cellular respiration is influenced by factors such as the availability of oxygen, the temperature, and the presence of inhibitors.
Cellular respiration is also tightly regulated to ensure that energy production matches the energy demands of the cell.
Comparison with Other Metabolic Pathways
Cellular respiration is distinct from other metabolic pathways, such as fermentation. Fermentation occurs in the absence of oxygen and produces lactic acid or ethanol as a byproduct. While fermentation is less efficient than cellular respiration, it allows cells to generate energy in oxygen-limited environments.
Role in Metabolism
Cellular respiration plays a central role in overall metabolism. It provides the energy required for various cellular processes, including protein synthesis, DNA replication, and cell movement. Cellular respiration also interacts with other metabolic pathways, such as glycolysis and gluconeogenesis, to maintain cellular homeostasis.
FAQ Corner: Which Of The Following Statements About Cellular Respiration Is True
What is the primary function of cellular respiration?
To generate energy for cells in the form of ATP.
What are the key stages of cellular respiration?
Glycolysis, Krebs cycle, and electron transport chain.
What is the role of glucose in cellular respiration?
Glucose is the primary fuel source, broken down to release energy.
How is ATP produced during cellular respiration?
Through the electron transport chain, using the energy released from glucose breakdown.
What factors influence the efficiency of cellular respiration?
Temperature, oxygen availability, and enzyme activity.