Unit 3 Circular Motion and Gravitation Worksheet Answers offers a comprehensive and engaging resource for students seeking a deeper understanding of these fundamental concepts. This guide provides a thorough overview of circular motion, centripetal force, gravitation, and their practical applications, empowering students with a solid foundation in these essential physics topics.
Delving into the intricacies of circular motion, the worksheet explores angular displacement, velocity, and acceleration, illustrating these concepts with real-world examples. It delves into the concept of centripetal force, explaining its role in maintaining circular motion and its relationship with mass and velocity.
Additionally, the worksheet provides a comprehensive examination of gravitation, introducing Newton’s law of universal gravitation and exploring gravitational interactions in the universe.
Circular Motion and Gravitation Worksheet Answers: Unit 3 Circular Motion And Gravitation Worksheet Answers
This worksheet covers the concepts of circular motion and gravitation, providing exercises to help students understand and apply these principles.
Circular Motion
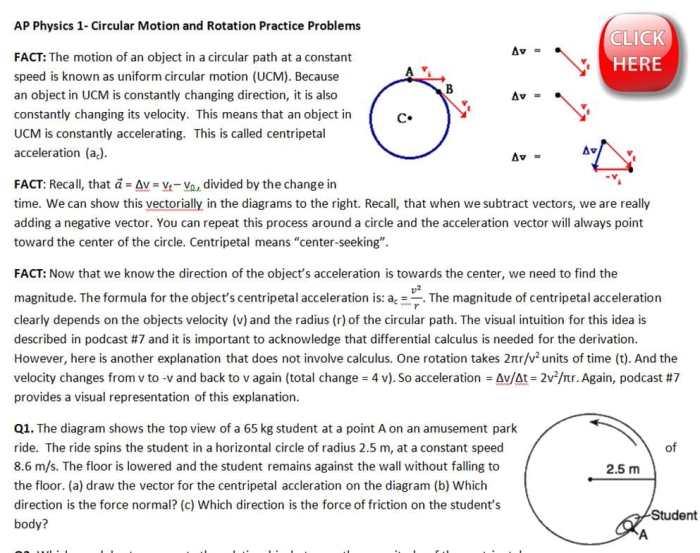
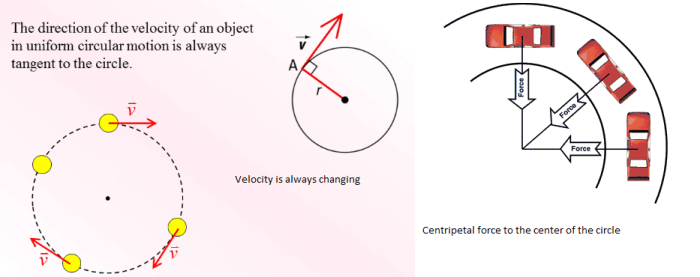
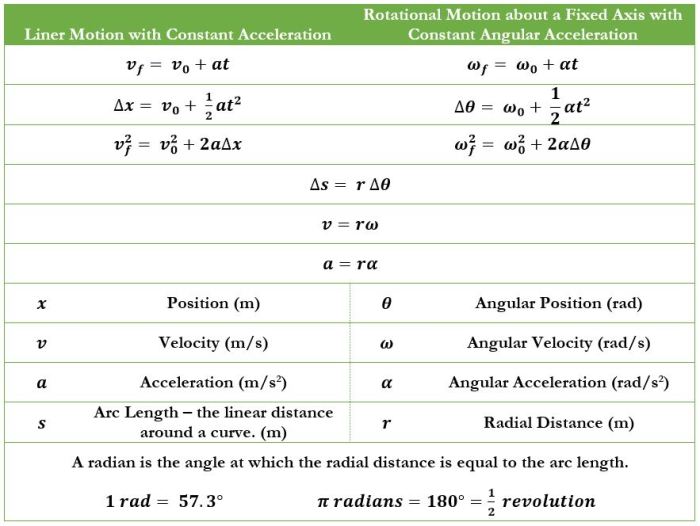
Circular motion occurs when an object moves in a circular path around a fixed point, called the center of rotation. Key characteristics include:
- Angular displacement: The angle swept out by the object
- Angular velocity: The rate of change of angular displacement
- Angular acceleration: The rate of change of angular velocity
Examples of circular motion include the motion of planets around the sun, the motion of a car on a curved road, and the motion of a spinning top.
Centripetal Force
Centripetal force is the force that keeps an object moving in a circular path. It is directed towards the center of rotation and is provided by an external force, such as gravity or friction.
The centripetal force is given by the equation:
Fc= mv 2/r
where:
- F cis the centripetal force
- m is the mass of the object
- v is the speed of the object
- r is the radius of the circular path
Gravitation, Unit 3 circular motion and gravitation worksheet answers
Gravitation is the force of attraction between any two objects with mass. It is described by Newton’s law of universal gravitation:
Fg= Gm 1m 2/r 2
where:
- F gis the gravitational force
- G is the gravitational constant (6.674 × 10 -11N m 2/kg 2)
- m 1and m 2are the masses of the two objects
- r is the distance between the centers of the two objects
Gravitation is responsible for holding the planets in orbit around the sun, the moon in orbit around the Earth, and for the formation of galaxies and stars.
Applications
Circular motion and gravitation have numerous practical applications:
- Engineering: Designing bridges, buildings, and machinery
- Physics: Studying the motion of planets, satellites, and other celestial bodies
- Astronomy: Understanding the formation and evolution of galaxies and stars
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of Unit 3 Circular Motion and Gravitation Worksheet Answers?
This worksheet provides a comprehensive guide to the concepts of circular motion, centripetal force, and gravitation, offering detailed explanations, examples, and exercises for enhanced understanding.
What topics are covered in this worksheet?
The worksheet covers circular motion, including angular displacement, velocity, and acceleration, as well as centripetal force and its relationship with mass and velocity. It also explores gravitation, Newton’s law of universal gravitation, and gravitational interactions.
How can this worksheet help me improve my understanding of circular motion and gravitation?
The worksheet provides clear explanations, engaging examples, and practice exercises that reinforce the concepts of circular motion and gravitation. It allows students to test their understanding and identify areas where further clarification is needed.